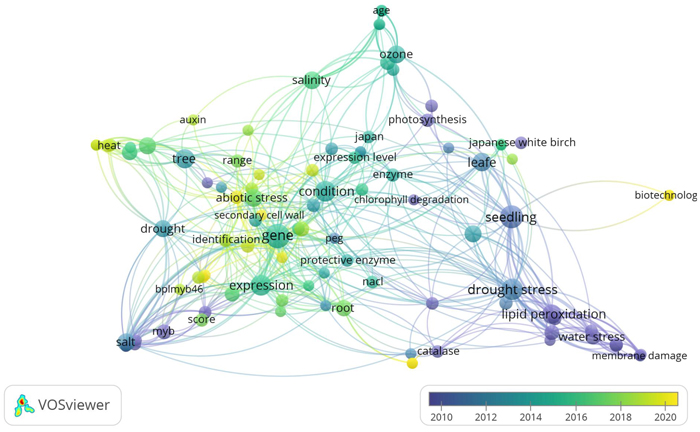
Fig. 1. Term co-occurrence map of physiological, biochemical, and molecular aspects in Betula platyphylla studies under abiotic stress using VOSviewer software (https://www.vosviewer.com/). VOSviewer analyzed text mining and bibliometric of scientific papers by observing the outputs of term (keyword) co-occurrence analysis. It is obvious that drought stress, heat, salinity, ozone, and water stress as well, are the most dominant abiotic stress, but the other key terms such as physiological and biochemical parameters belong to the other terms.
| Table 1. The information of antioxidant enzymes that are used as potential markers of abiotic stress tolerance in Betula platyphylla. All studies were conducted in China from 2017–2020. | |||
| Antioxidant enzymes | Type of abiotic stress | Response | References |
| SOD, POD | salt and osmotic stress | SOD and POD content in BpMYB46 OE lines increased under salt and osmotic stress | (Guo et al. 2017b) |
| SOD, POD | drought stress | SOD and POD increased in BpARF1 RNAi plant under drought stress | (Li et al. 2020a) |
| SOD, POD | heat stress | SOD and POD content in BpHSP9 OE lines increased under heat stress | (Liu et al. 2018) |
| SOD, POD | cold stress | SOD and POD content in BPERF13 OE lines increased under cold stress | (Lv et al. 2019) |
| SOD, POD | osmotic stress | SOD and POD content in BpHOX2 OE lines increased under osmotic stress | (Tan et al. 2020) |
| SOD, POD, GST | salt and osmotic stress | SOD, POD, and GST content in BplMYB46 and BplMYB13 OE lines increased under salt and osmotic stress | (Wang et al. 2019b) |
| SOD, POD | salt stress | SOD and POD content increased under salt stress in Betula platyphylla | (Mijiti et al. 2017) |
| SOD: Superoxide dismutase; POD: Peroxidase; GST: Glutathione S-transferase; BplMYB46: Betula platyphylla myeloblastosis 46 gene; BpHOX2: B. platyphylla homeobox-leucine zipper 2 gene; BpHSP9: B. platyphylla heat shock protein 9 gene; BpUVR8: B. platyphylla UV resistance locus 8 gene; BpERF13: B. platyphylla ethylene response factor 13 gene; BpMYB13: B. platyphylla myeloblastosis 13 gene; BpARF1: B. platyphylla auxin response factor 1 gene. | |||
| Table 2. The summary of cis-acting element of Betula platyphylla related to abiotic stress genes. | ||||
| No | Gene name | cis-acting element | Target genes | Reference |
| 1 | BplMYB46 | - TC-BOX ((T(G/A)TCG(C/G))) - GT-BOX (A(G/T)T(A/C)GT(T/G)C) - E-BOX ((CA(A/T/C)(A/G/C)TG) | - SOD gene - POD gene, PAL gene | (Guo et al. 2018) |
| 2 | BplMYB46 | - MYBCORE: CAGTTA - AC-box: ACCACCT | - SOD, POD, and GST | (Guo et al. 2017b; Wang et al. 2019b) |
| 3 | BpHSP | - TATA box - heat shock element (5’-AAAAAATTTC-3’) | - N.A. | (Liu et al. 2018) |
| 4 | BpARF | - 2010 bp upstream of the 5-UTRs of the BpARF genes, including: 1. abscisic acid responses 2. anaerobic induction 3. auxin responses 4. cell cycle regulation 5. gibberellin responses 6. light responses 7. methyl jasmonate (MeJA) responses 8. MYBHv1 binding 9. MYB binding in response to drought 10. salicylic acid responses 11. defense and stress responses 12. meristem expression 13. MYB binding in response to light and low-temperature responses | - N.A. | (Li et al. 2020a) |
| 5 | BpUVR8 | - The jasmonic acid methyl ester response element (CGTCA-motif) - Abscisic acid response element (ABRE) - Auxin response element (CATATG-motif) - Drought-induced response elements (MBS) - Low-temperature, heat stress - Anaerobic response elements | - N.A. | (Li et al. 2018) |
| 6 | BpERF13 | - LTRECOREATCOR15 (CCGAC):CAGGCGTCGG - MYBCORE (CNGTTR): TCAACAGGAT | - POD6 and POD8 gene - SOD1, SOD3, POD6, POD8, CBF3 and CBF4 | (Lv et al. 2019) |
| 7 | BpHOX2 | - Dehydration responsive element “RCCGAC” - Mybp binding box “CCWACC” - Novel cis‐acting elements with the sequences of “AAGAAG” - Novel cis‐acting elements with the sequences of “TACGTG” | - N.A. | (Tan et al. 2020) |
| 8 | BpERF11 | - GCC boxes - DRE motifs | - SODs, PODs, P5CS, P5CDH, PRODH, MYB61, DHN, and LEAs | (Zhang et al. 2016) |
| 9 | BpNAC012 | - The core sequence CGT[G/A] - The SNBE site | - P5CS1, P5CS2, SODs, PODs - Secondary wall biosynthesis genes (lignin, cellulose, xylem) and wood associated TF genes (MYB46, MYB54, MYB63, MYB85, KNAT7) | (Hu et al. 2019) |
| BplMYB46: Betula platyphylla myeloblastosis 46 gene; BpHOX2: B. platyphylla homeobox-leucine zipper 2 gene; BpHSP9: B. platyphylla heat shock protein; BpUVR8: B. platyphylla UV resistance locus 8 gene; BpERF13: B. platyphylla ethylene response factor 13 gene; BpERF11: B. platyphylla ethylene responsive factor 11 gene; BpARF1: B. platyphylla auxin response factor gene; BpNAC012: B. platyphylla No apical meristem (NAM), Arabidopsis transcription activation factor (ATAF1/2), Cup-shaped cotyledon (CUC2) 12 gene; SODs: Superoxide dismutase; PODs: Peroxidase; PALs: Phenylalanine ammonia lyase; GSTs: Glutathione S-transferase; CBFs: C-repeat binding factors; P5CS: Delta-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase; P5CDH: Delta-1 pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase; PRODH: Proline dehydrogenase; MYBs: Myeloblastosis genes; DHN: dehydration gene; LEAs: Late embryogenesis abundant; KNAT7: Knotted-like homeobox of Arabidopsis thaliana 7; SNBE: Secondary wall NAC binding element; N.A.: no detailed comments. | ||||
| Table 3. The summary of candidate genes for Betula platyphylla under abiotic stress. | ||||||||
| No | Family of TF/gene/miRNAs | Gene name | Species | Type of abiotic stress | Degree/ dose | Location | Application | References |
| 1 | MYB | - BplMYB46 | - Betula platyphylla | - Drought stress | N.A. | - nucleus | - BplMYB46 bind to MYBCORE in transgenic B. platyphylla, indicating BplMYB46 may contribute to drought stress. | (Guo et al. 2017b) |
| 2 | - AHL | - B. halophila | - Salt stress | 200 mM of NaCl for 24 h | - nucleus | - AHL gene was the most up-regulated gene in leaves under salt stress, indicating that the AHL gene might contribute in response to salt stress in B. halophila. | (Shao et al. 2018) | |
| - DHNs | - B. halophila | - Salt stress | 200 mM of NaCl for 24 h | - nucleus | - Dehydrin-1 gene was up-regulated gene in leaves after salt stress, indicating that dehydrin-1 gene might contribute to the response to salt stress in B. halophila. | (Shao et al. 2018) | ||
| 3 | miRNAs (miR395c-3p) | - B. luminifera | - Heat stress | - 0.5 h and 4 h | - N.A. | - miRNAs (miR395c-3p) were up-regulated under heat stress in B. luminifera, suggesting that miR395c-3p contribute to improving heat tolerance in other birches such as B. platyphylla. | (Pan et al. 2017a) | |
| 4 | NAC | - BpNAC5, - BpNAC6 BpNAC7, BpNAC8 - BpNAC13, BpNAC14, BpNAC15, BpNAC19, BpNAC21 | - B. platyphylla | - Drought, salt, dehydration, osmotic and ABA treatment | - N.A. | - nucleus and C-terminal | - Multiple copies of MBS, W-box and ABRE were found in the promoters of BpNACs, implying that these genes might play important roles in stress responses. | (Guo et al. 2017a) |
| 5 | UVR | - BpUVR8 | - B. platyphylla | - ABA treatment - Salt stress | - 10 μM ABA for 24 h - 100 mM NaCl for 24 h | - nucleus | - BpUVR8, as a specific receptor for UV-B, is regulated by salt stress and ABA treatment. It is also suggested that the UVR8 gene may be involved in the early signal transduction of salinity and ABA stress in addition to the process of UV-B signal transduction. | (Li et al. 2018) |
| MYB: Myeloblastosis; miRNAs: microRNAs; NAC: No apical meristem (NAM ), Arabidopsis transcription activation factor (ATAF1/2), Cup-shaped cotyledon (CUC2); UVR: UV resistance; BplMYB46; AHL: AT-Hook Motif Nuclear Localized; DHNs: Dehydrin-1; BpNACs: Betula platyphylla No apical meristem (NAM); BpUVR8: B. platyphylla UV resistance locus 8 gene; ABA: Abscisic acid; NaCl: Sodium chloride; MBS: MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility; ABRE: Abscisic acid-responsive; N.A.: no detailed comments. | ||||||||
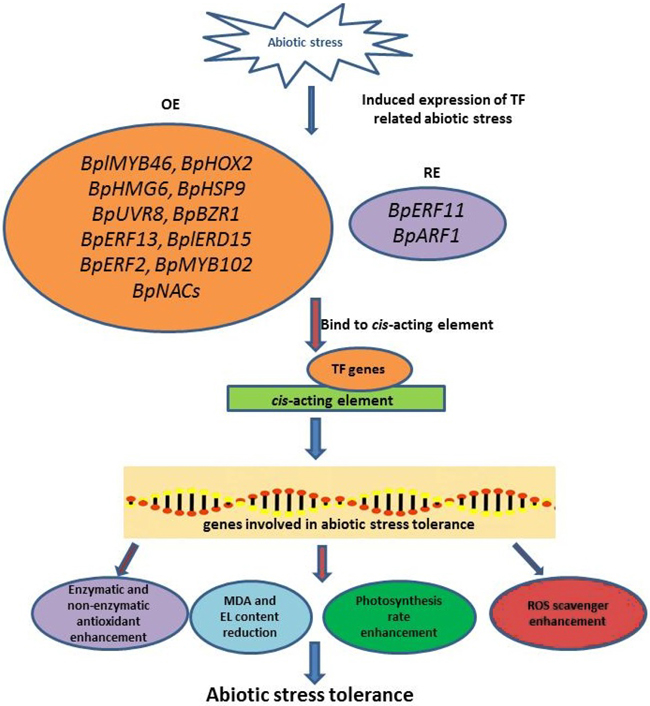
Fig. 2. The illustration of abiotic stress tolerance mechanism in Betula platyphylla. Abiotic stress-induced the expression of TF-related abiotic stress. Several TFs will be overexpressed or repress-expressed and followed binding to cis-acting elements to induce the expression of genes involved in abiotic stress tolerance. These genes involved in abiotic stress tolerance affects the plant response in physiological and biochemical aspect. BplMYB46: B. platyphylla myeloblastosis 46 gene; BpHOX2: B. platyphylla homeobox-leucine zipper 2 gene; BpHMG6: B. platyphylla high-mobility group 6 gene; BpHSP9: B. platyphylla heat shock protein 9 gene; BpUVR8: B. platyphylla UV resistance locus 8 gene; BpBZR1: B. platyphylla brassinazole-resistant 1 gene; BpERF13: B. platyphylla ethylene response factor 13 gene; BplERD15: B. platyphylla early response to dehydration 15 gene; BpERF2: B. platyphylla ethylene response factor 2 gene; BpMYB102: B. platyphylla myeloblastosis 102 gene; BpERF11: B. platyphylla ethylene responsive factor 11 gene; BpARF1: B. platyphylla auxin response factor 1 gene; BpNACs: B. platyphylla No apical meristem (NAM), Arabidopsis transcription activation factor (ATAF1/2), Cup-shaped cotyledon (CUC2) genes; MDA: Malondialdehyde; EL: Electrolyte leakage; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.