| Table 1. Description of the operational chains in Finnish forestry used in the expert survey. Please not that not all the alternatives within a chain are shown. For instance, the possible mixed tree species, usage of of nursery seedlings, need for weeding, possible fertilization or cuttings for seed tree removal are not listed here. | |||||||
| Chain | Strategy | Part of Finland | Tree species | Cutting method | Site type | Soil preparation | Regeneration |
| 1 | even aged | south | pine | clearcut | xeric/sub-xeric | harrowing/scalping | sowing |
| 2 | even-aged | south | pine | clearcut | sub-xeric | mounding | planting |
| 3 | even-aged | south | pine | seedling tree felling | sub-xeric | harrowing | natural |
| 4 | even-aged | south | pine | clearcut | mesic | harrowing/scalping | planting |
| 5 | even-aged | south | spruce | clearcut | herb-rich | no | planting |
| 6 | even-aged | south | spruce | clearcut | herb-rich | mounding | planting |
| 7 | even-aged | south | spruce | strip felling | herb-rich | no | natural |
| 8 | even-aged | south | spruce | strip felling | herb-rich | harrowing | natural |
| 9 | even-aged | south | spruce | shelterwood felling | herb-rich | no | natural |
| 14 | even-aged | north | pine | clearcut | xeric | harrowing | sowing |
| 15 | even-aged | north | pine | seedling tree felling | xeric | no | natural |
| 16 | even-aged | north | pine | seedling tree felling | xeric | harrowing | natural |
| 17 | even-aged | north | pine | clearcut | mesic/ sub-xeric | mounding | planting |
| 18 | even-aged | north | pine | clearcut | mesic/sub-xeric | harrowing | sowing |
| 19 | even-aged | north | pine | clearcut | mesic | harrowing | planting |
| 20 | even-aged | north | pine | seedling tree felling | sub-xeric | harrowing | natural |
| 21 | even-aged | north | spruce | clearcut | herb-rich rich/mesic | mounding | planting |
| 22 | even-aged | north | spruce | strip felling | herb-rich | no | natural |
| 23 | even-aged | north | spruce | strip felling | herb-rich | harrowing | natural |
| 24 | uneven-aged | south | pine | patch felling | xeric | no/light scalping | natural |
| 25 | uneven-aged | south | pine | patch felling | sub-xeric | no/light scalping | natural |
| 26 | uneven-aged | south | pine | selection felling | mesic | no | undergrowth |
| 27 | uneven-aged | south | pine | selection felling | mesic | no | natural |
| 28 | uneven-aged | south | spruce | patch felling | herb-rich rich/mesic | no/light scalping | natural |
| 29 | uneven-aged | south | spruce | selection felling | herb-rich rich/mesic | no | undergrowth |
| 30 | uneven-aged | north | pine | selection felling | sub-xeric | no | natural |
| 31 | uneven-aged | north | pine | patch felling | mesic | no/light scalping | natural |
| 32 | uneven-aged | north | spruce | patch felling | herb-rich | no/light scalping | natural |
| 33 | uneven-aged | north | spruce | selection felling | herb-rich | no | undergrowth |
| 34 | uneven-aged | north | spruce | selection felling | mesic | no | undergrowth |
| 35 | uneven-aged | north | spruce | patch felling | mesic | no/light scalping | natural |
| 36 | uneven-aged | south | pine | selection felling | sub-xeric | no | natural |
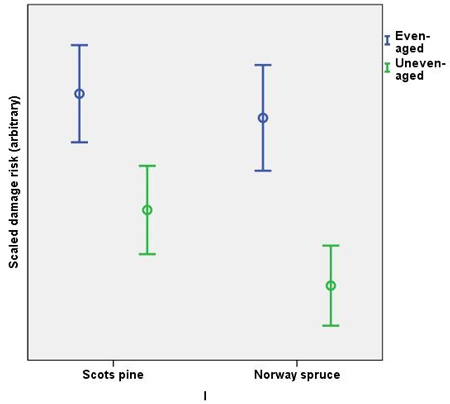
Fig. 1. Scaled damage risks in the management regimes by main tree species. All damage causes combined. The error bars show 95% confidence intervals, but the actual scale of the arbitrary y-axis is not shown.
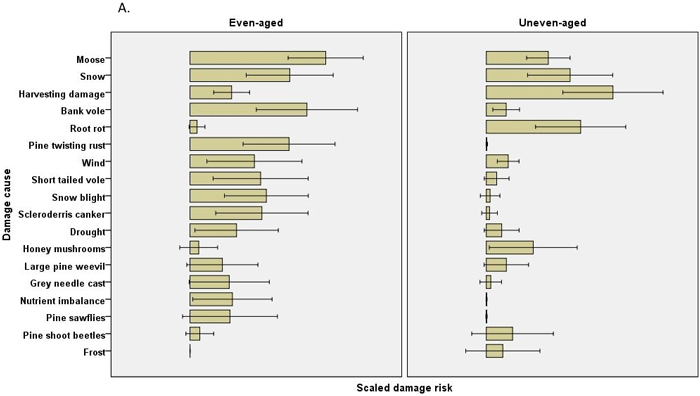
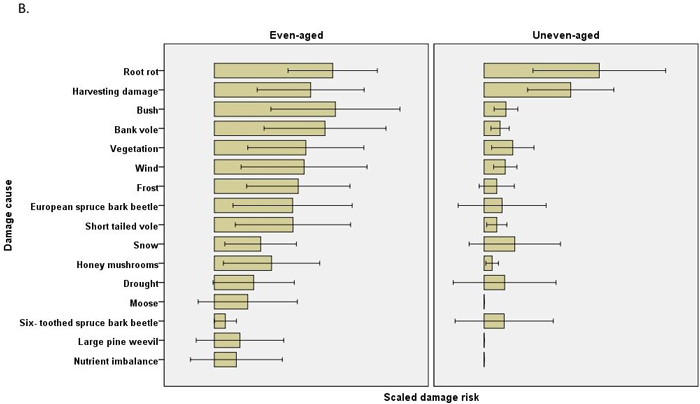
Fig. 2. The risks (scaled damage risks) by damage causes by management regimes and by main tree species: A) Scots pine B) Norway spruce. The error bars show 95% confidence intervals, but the actual scale of the arbitrary x-axis is not shown.
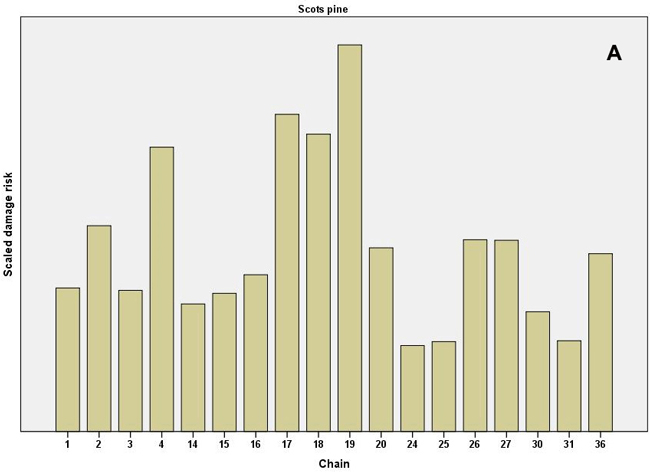
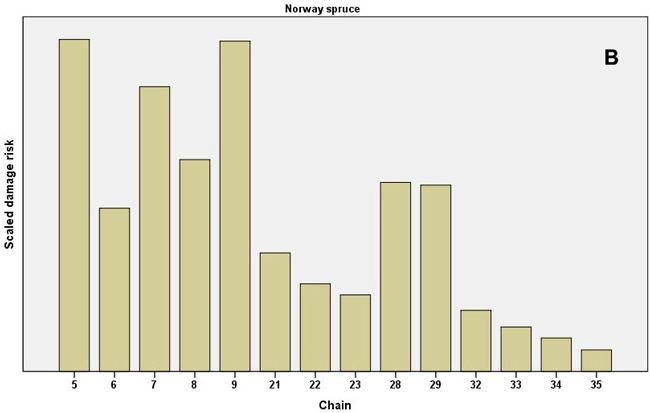
Fig. 3. Scaled damage risks by the operational chains used in the expert survey. All damage causes combined. A) Scots pine as the main tree species and B) Norway spruce as the main tree species. For description of the chains, see Table 1. Chains 24–36 present uneven-aged chains, as shown.
| Table 2a. Risk of damage (scaled damage risk) by the causal agent and operational chain, in chains with Scots pine as the main tree species. Risk classes: L = low risk M = medium risk, H = high risk. The risk classes are based on percentiles of the scaled damage risks of the specific cause in all the chains: 51–70 percentiles present a medium risk and percentiles over 70 a high risk. For a description of the chains, please see Table 1. | |||||||||||||||||
| Damage cause | Chain number (even-aged management) | Chain number (uneven-aged management) | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 30 | 31 | 36 | |
| Drought | H | H | H | L | M | L | L | M | L | L | M | L | M | M | L | L | L |
| Frost | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | H | L | L | L | L | L |
| Nutrient imbalance | L | H | L | H | L | L | L | M | L | H | L | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Snow | M | M | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | M | M | H | H | H | H | H |
| Wind | L | L | H | L | L | H | H | M | L | H | M | L | M | M | M | L | M |
| Large pine weevil | M | L | L | L | L | L | M | L | H | M | M | M | L | L | L | L | M |
| Pine sawflies | H | H | H | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Pine shoot beetle | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | M | L | L | L | H | L | L | |
| Harvesting damage | M | M | H | M | L | M | M | M | M | H | M | M | H | H | H | M | H |
| Bush | M | H | M | H | L | L | L | M | L | M | L | M | L | M | L | M | L |
| Vegetation | M | M | H | H | L | L | L | M | H | M | L | M | L | M | L | M | H |
| Bank vole | H | H | M | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | M | M | L | L | M | M | M |
| Short tailed vole | M | M | L | M | M | M | M | H | H | H | L | L | L | L | L | M | M |
| Moose | M | H | H | H | M | M | H | H | H | H | M | H | H | M | H | H | L |
| Grey needle cast | L | M | L | M | L | L | L | H | L | H | L | L | L | L | L | M | L |
| Honey mushrooms | L | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | M | L | H | H | L | M | M |
| Pine twisting rust | M | H | L | H | L | L | M | H | H | H | L | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Resin-top disease | L | L | L | M | L | L | L | H | M | H | L | L | M | M | L | L | L |
| Root rot | L | L | M | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | M | H | H | H | L | L | H |
| Scleroderris canker | H | H | L | H | L | H | M | H | H | M | L | L | L | L | M | L | L |
| Snow blight | L | M | L | H | H | H | H | H | M | L | L | L | L | M | H | L | |
| Table 2b. Risk of damage (scaled damage risk) by the causal agent and operational chain, in chains with Norway spruce as the main tree species. Risk classes: L = low risk M = medium risk, H = high risk. The risk classes are based on percentiles of the scaled damage risks of the specific cause in all the chains: 51–70 percentiles present a medium risk and percentiles over 70 a high risk. For a description of the chains, please see Table 1. | ||||||||||||||
| Damage cause | Chain number (even-aged management) | Chain number (uneven-aged management) | ||||||||||||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 28 | 29 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | |
| Drought | L | M | M | L | L | H | L | L | L | H | L | L | L | L |
| Frost | H | M | H | H | M | M | M | M | M | L | M | L | L | L |
| Nutrient imbalance | L | L | L | L | L | H | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Snow | H | L | H | L | M | M | M | M | M | M | H | L | L | L |
| Wind | L | L | H | H | H | L | H | H | L | M | M | M | M | M |
| European spruce bark beetle | M | M | H | H | L | L | L | L | M | L | L | L | L | L |
| Large pine weevil | H | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Six toothed spruce bark beetle | L | M | M | M | L | L | L | L | M | L | L | L | L | L |
| Harvesting damage | M | M | H | H | H | L | M | M | H | H | L | M | M | L |
| Bush | H | L | H | H | H | L | M | L | M | M | M | M | L | L |
| Vegetation | H | L | H | M | H | L | M | L | M | M | M | M | L | L |
| Bank vole | H | H | M | M | M | H | M | M | M | L | M | M | L | L |
| Short tailed vole | H | H | M | M | M | H | M | M | M | M | L | L | L | L |
| Moose | H | H | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Honey mushrooms | M | M | M | M | H | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Root rot | H | H | H | H | H | L | L | L | H | H | L | L | L | L |
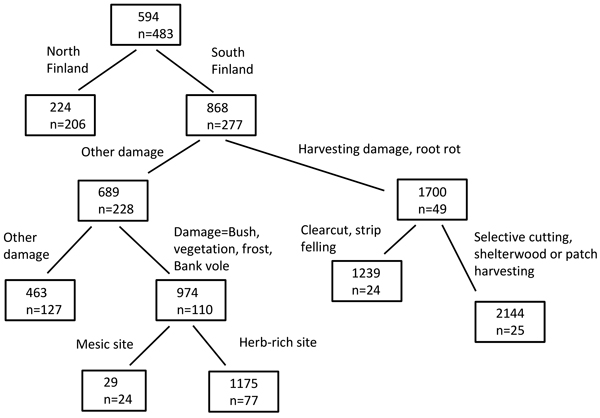
Fig. 4. Example of a regression tree, computed with rpart package in R. The scaled damage risk was used as the response variable, and combinations of operational methods, site factors, damage causes and cutting methods were used as classifiers. The numbers in the box show the risk value (scaled damage risk) and n indicates the number of risk assessments (by all experts and for the appropriate damage causes and operational chains).
| Table 3. The 10 most risky operations (question B), based on the votes given by the experts). EA = even-aged, UEA = uneven-aged management. Votes means the votes given by all experts for all damage causes. | |||
| Regime | Tree Species | Operation | Votes |
| EA | Scots pine | Clearcutting | 67 |
| UEA | Scots pine | Selection cutting | 66 |
| EA | Norway spruce | Thinning | 62 |
| EA | Scots pine | Thinning | 54 |
| EA | Norway spruce | Strip felling | 46 |
| EA | Scots pine | Planting | 41 |
| UEA | Norway spruce | Patch harvesting | 39 |
| EA | Norway spruce | No soil preparation | 36 |
| UEA | Norway spruce | Selection cutting | 33 |
| EA | Norway spruce | Clearcutting | 33 |
| Table 4. Comparison of damage risks between even-aged (EA) and uneven-aged (UEA) management regimes according to the literature review and the expert survey. Blank cells in the literature review columns indicate no data. The comparisons in the expert survey are based on the scaled damage risk. The risk values over two times higher or lower depicted a higher or lower risk, respectively. Values five times higher or lower depicted a much higher or lower risk. ’>>’ denotes a much higher risk and ‘<<’ a much lower risk. The most obvious discrepancies between the literature and the expert survey are underlined. | |||
| Main tree species | Damage cause | Comparison of damage risks in EA and UEA in the literature review | Comparison in the expert survey |
| Sots pine | Drought | Seedling damage may be higher in EA | EA > UEA |
| Frost | Seedling damage may be higher in EA | EA << UEA | |
| Nutrient imbalance | Increased risk in former peatlands in EA | EA >> UEA | |
| Snow | EA = UEA | ||
| Wind | Higher risk in EA | EA > UEA | |
| Large pine weevil | Higher risk in EA | EA = UEA | |
| Pine sawflies | No unambiguous data | EA >> UEA | |
| Pine shoot beetles | No clear differences | EA = UEA | |
| Harvesting damage | Usually low risk in EA and UEA | EA < UEA | |
| Bush | EA > UEA | ||
| Vegetation | EA = UEA | ||
| Bank vole | EA >> UEA | ||
| Short tailed vole | Planted seedlings: higher risk in EA | EA >> UEA | |
| Moose | Higher damage in EA seedling stands | EA > UEA | |
| Grey needle cast | Higher risk in EA in too fertile soils | EA >> UEA | |
| Honey mushrooms | No clear differences | EA < UEA | |
| Pine twisting rust | EA >> UEA | ||
| Resin- top disease | EA > UEA | ||
| Root rot | High risk in EA and UEA | EA << UEA | |
| Scleroderris canker | Higher risk in EA | EA >> UEA | |
| Snow blight | EA >> UEA | ||
| Norway spruce | Drought | Seedling damage may be higher in EA | EA = UEA |
| Frost | Seedling damage may be higher in EA | EA >> UEA | |
| Nutrient imbalance | Higher risk in EA | EA >> UEA | |
| Snow | EA = UEA | ||
| Wind | Higher risk in EA | EA > UEA | |
| European spruce bark beetle | Higher risk in EA | EA > UEA | |
| Large pine weevil | Higher risk in EA | EA >> UEA | |
| 6- toothed spruce bark beetle | No clear differences | EA = UEA | |
| Harvesting damage | Repeated thinnings: high risk in UEA | EA = UEA | |
| Bush | EA >> UEA | ||
| Vegetation | EA > UEA | ||
| Bank vole | EA >> UEA | ||
| Short tailed vole | Planted seedlings: higher risk in EA | EA >> UEA | |
| Moose | Small risk in EA and UEA | EA >> UEA | |
| Honey mushrooms | No unambiguous data | EA >> UEA | |
| Root rot | High risk in EA and UEA | EA = UEA | |