| Table 1. Potential benefits of forest data including potential conflicts. | ||||
| Category of benefit | Type of data | Users of data | Examples of benefits | Potential conflicts |
Enhanced ecological functions | Biodiversity data: data on species, ecosystems, biodiversity | Forest owners, citizens, environmental non-governmental NGOs (non-governmental organizations) | More efficient conservation of forest species and biotopes, designation of critical habitat | -Limitations for forest owners OR new income opportunities for forest owners through ecological compensation markets |
Carbon flow and carbon stock data | Forest owners, citizens, environmental NGOs | More efficient carbon sequestration and storage | Limitations for forest owners OR new income opportunities for forest owners through carbon markets | |
Enhanced benefits from bioeconomy products | Timber data + forest management plans | Forest owners, forest service companies, forest industry, tourism industry | More efficient and sustainable forestry, new business opportunities, growth and jobs | Possible negative impacts for non-owners: weaker recreation possibilities, weaker destination quality for tourism OR possibility to negotiate |
Data on non-wood forest resources, e.g., berries, mushrooms | Berry pickers, mushroom collectors, non-wood forest product companies, tourism companies | More efficient gathering, enhanced food supplies, new income opportunities, new business opportunities, growth and jobs | Possible nuisance for forest owners and for protective former collectors OR possibility to negotiate | |
Enhanced benefits from experiences | Data on touristic sites: nature types, landscapes, routes, sports, history etc. | Recreational users, tourists, hunters, destination marketers | Enhanced recreational experiences, “nowness” (real-time, data-driven, customer-centric co-creation), wellbeing, new business opportunities, growth and jobs | -Possible overcrowding: disturbance to wildlife, wearing of terrain |
Enhanced protection against forest threats and disturbances | Data on forest pests, pathogens, fires and storms | Forest owners, all forest users, insurance companies, forest protection companies | Enhanced forest protection, i.e., more effective threat management, new business opportunities, growth and jobs | Species connected to wildfires may need support |
Enhanced democracy | All forest data | Citizens, NGOs, companies, business researchers, educators | Participation, transparency, enhanced monitoring, knowledge, legitimacy, realization of rights, governance mechanisms | |
| Table 2. Benefits of forest data and relevant forest-related and other rights. | |||
Enhanced ecological functions | Enhanced product innovation | Enhanced experience innovation | Enhanced democracy |
Protection against threats and disturbances = enhanced ecological functions, products, and experiences | |||
Right to a healthy environment | Property rights of forest owners | Participatory rights | |
Indigenous rights | |||
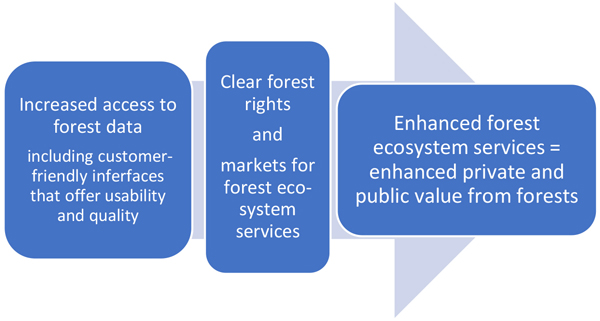
Fig. 1. Data, rights, and markets for enhanced forest ecosystem services.