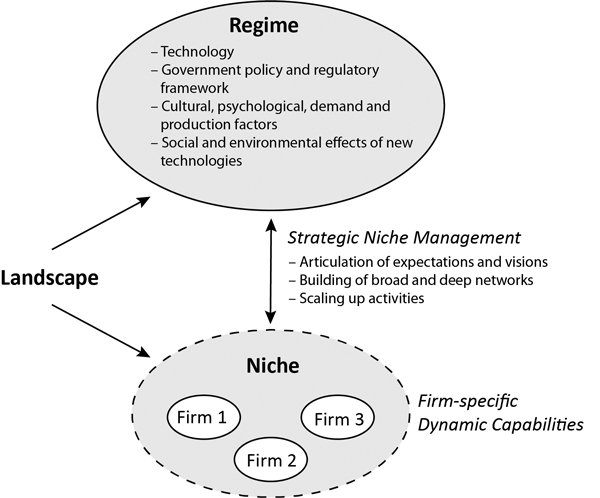
Fig. 1. Theoretical model of the study. The studied companies are part of a loose niche that operates beyond the forest-based regime. The success of the companies is the result of both niche–regime dynamics and the companies’ internal dynamic capabilities.
| Table 1. Characteristics of the studied small and medium-sized companies (SMEs) utilizing wood-based side streams and interviewees’ positions within the companies. B2B: business-to-business; B2C: business-to-consumers; CEO: chief executive officer. | |||
| Firm | Firm maturity | B2B vs. B2C | Interviewee position |
| 1 | 5–10 years | B2B | CEO, founder |
| 2 | 5 years | B2B | Development & quality manager |
| 3 | 15–20 years | B2C | CEO |
| 4 | 20–30 years | B2B | Chairman of the board |
| 5 | <5 years | B2B | CEO, founder |
| 6 | <5 years | B2B | CEO, founder |
| 7 | 10–15 years | B2C | CEO |
| 8 | >50 years | B2C | Development manager |
| 9 | 0–5 years | B2C/B2B | CEO |
| 10 | 0–5 years | B2B | Chief technology officer, founder |
| Table 2. Frequencies of coding categories in the directed content analysis of the interviews with SMEs utilizing wood-based side streams. n = the number of interviewees mentioning the theme. | |
| 1. Organizational capabilities | n |
| Organization structure | |
| Decentralization | 4 |
| Organizational culture | |
| Openness, trust, flexibility, agility | 7 |
| ’Dare to disagree’ ethos | 3 |
| Diversity of backgrounds | 10 |
| Values | 6 |
| Employee commitment and loyalty | 5 |
| Leadership | 5 |
| Organizational routines and practices | |
| Learning, access to information, expertise | 6 |
| Integration of employees in decision-making | 3 |
| Customer understanding | 3 |
| Innovativeness | 10 |
| Routines for innovations | 8 |
| Incentives, human resource management | 4 |
| Formality and hierarchy of processes | 5 |
| 2. Niche-level activities | |
| Articulation of expectations and visions | |
| Core vision | 10 |
| The role of the cascading principle | 4 |
| Building broad and deep networks | |
| Partnerships, networks and cooperation to achieve the aims of the CBE | 9 |
| Deep vs. broad partnerships | 7 |
| Acquiring resources from networks | 4 |
| Partnerships with end-users and customers | 4 |
| Partnerships with regime actors | 4 |
| Innovations resulting from partnerships | 4 |
| Scaling-up | |
| Growth strategy | 7 |
| Market creation | 7 |
| From niche to regime substitution | 4 |
| 3. Learning processes | |
| Technological factors | |
| Quality of raw material, maintaining stable quality | 7 |
| Understanding the behavior of materials | 3 |
| Government policy and regulatory framework | |
| Standardization, labelling | 3 |
| Patents | 7 |
| Categorization | 4 |
| Monitoring in public procurements | 2 |
| Legislation | 6 |
| Extended producer responsibility | 4 |
| Cultural and psychological factors | |
| Credibility | 6 |
| Demand factors (customers/consumers) | |
| Customer acceptance | 4 |
| Brand building and communication | 5 |
| Customer willingness to pay premium | 3 |
| Production factors | |
| Production technology renewal | 3 |
| Production ecosystems | 5 |
| Access to financial capital | 5 |
| Availability of raw material | 6 |
| Price of raw material | 3 |
| Designing for circularity | 3 |
| Social and environmental effects of new technologies | |
| Evidence of environmental performance | 2 |